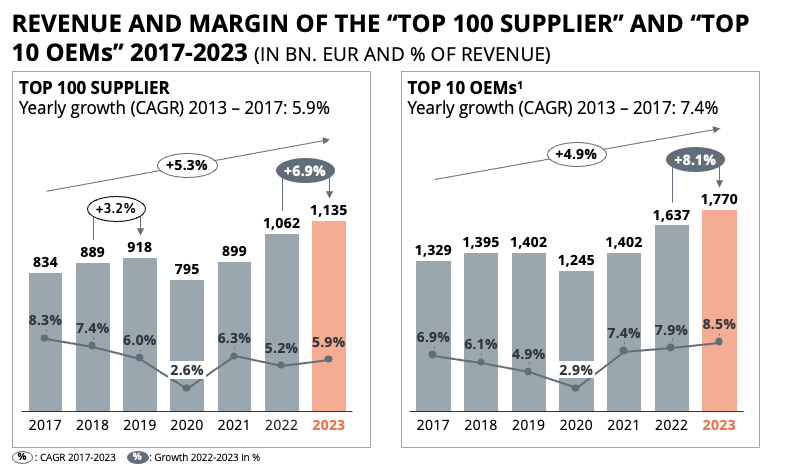
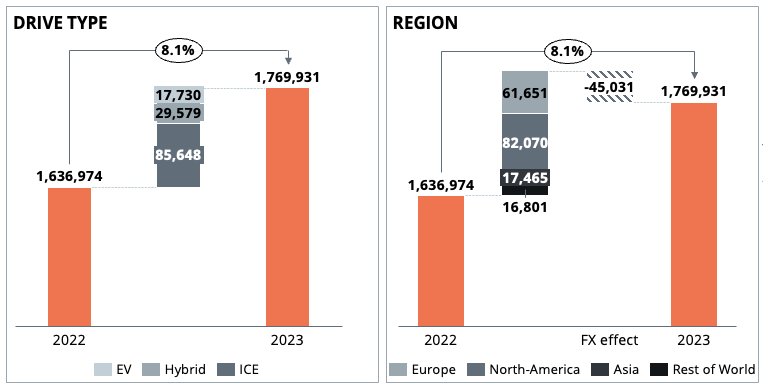
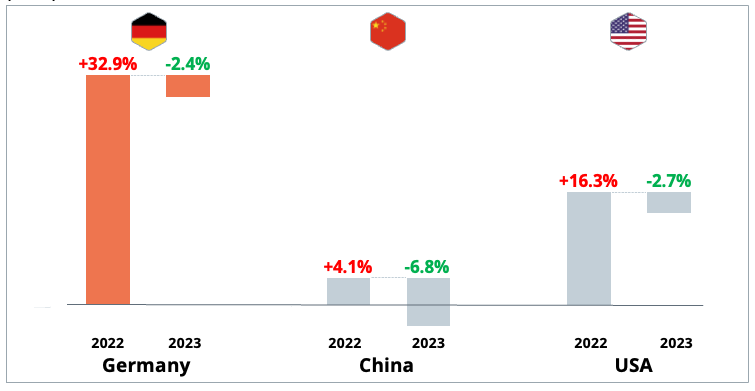
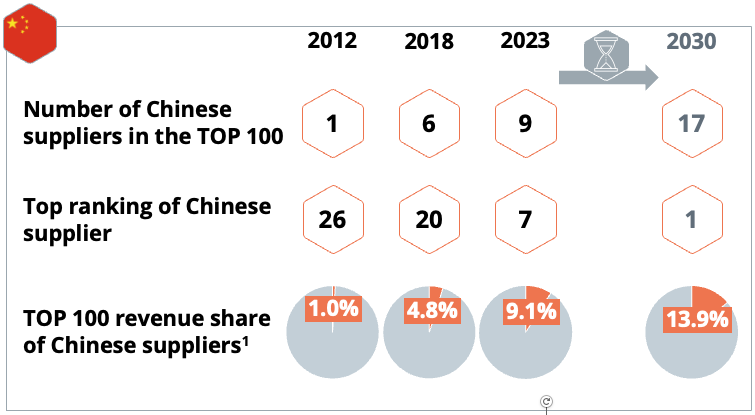
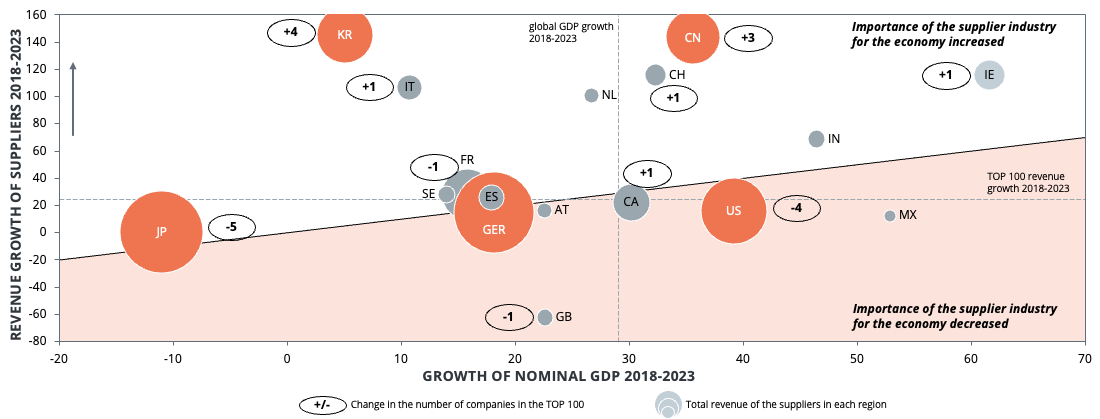
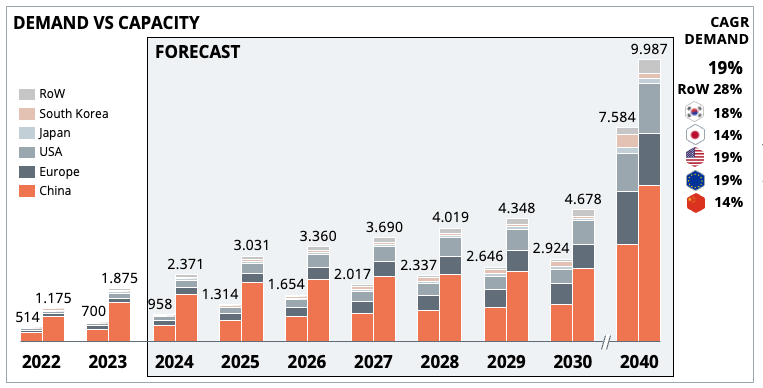
Dr. Alexander Timmer (1981) joined Berylls by AlixPartners (formerly Berylls Strategy Advisors), an international strategy consultancy specializing in the automotive industry, as a partner in May 2021. He is an expert in market entry and growth strategies, M&A and can look back on many years of experience in the operations environment. Dr. Alexander Timmer has been advising automotive manufacturers and suppliers in a global context since 2012. He has in-depth expert knowledge in the areas of portfolio planning, development and production. His other areas of expertise include digitalization and the complex of topics surrounding electromobility.
Prior to joining Berylls Strategy Advisors, he worked for Booz & Company and PwC Strategy&, among others, as a member of the management team in North America, Asia and Europe.
After studying mechanical engineering at RWTH Aachen University and Chalmers University in Gothenburg, he earned his doctorate in manufacturing technologies at the Machine Tool Laboratory of RWTH Aachen University.